Six Sigma Introduction
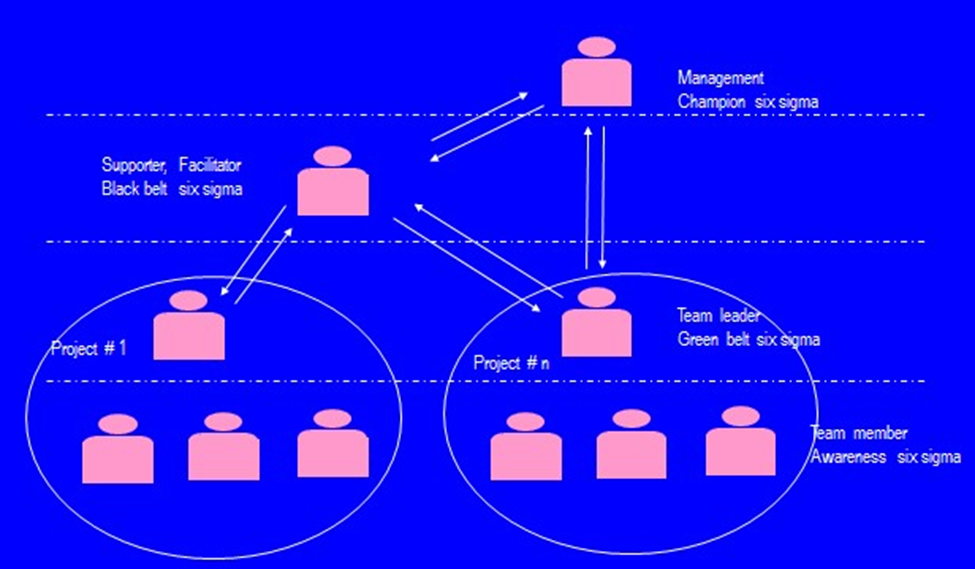
six sigma model

What is six sigma?
Sigma ( s ) is Greek letter used to indicate standard deviation
– A sigma level provides a statistical estimation of the the defect (error) rate
– Six sigma relates to 3.4 Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO)
2 ways of implementing six sigma
– As a management philosophy, e.g. General Electric
– As a quality tool for problem solving , most of companies are using it in this way
Six Sigma Origins
�In 80�s, a Motorola engineer found that less than 5% of the products reached the final station without any repair with a big impact on productivity & repair costs
�The engineers decided that the traditional way of measuring defect rate (%) is not satisfying, instead to measure defects per million opportunities
�Motorola developed this new concept and created the methodology, which named Six Sigma
– As a continuous improvement tools
The results for MOTOROLA� up till 2003
�Spent $70 million on quality related education
�In 1988, won Malcolm Baldrige (the USA quality award)
�Productivity increased average of 12% /yr
�Cost of quality reduced by more than 84%
�99.7% of in-process defects eliminated
�$16 billion in manufacturing costs saved
General Electric Six Sigma Deployment
�Capacity improvement of 12-18%
�Rise in operating margin to 16.7%
�$750 million in saving
�
GE Capital Mortgage Insurance
�Cut defects 96%
�Claim payments were reduced by $8M, while borrowers were offered alternatives to foreclosure
�Reported a 160% increase in new transactions
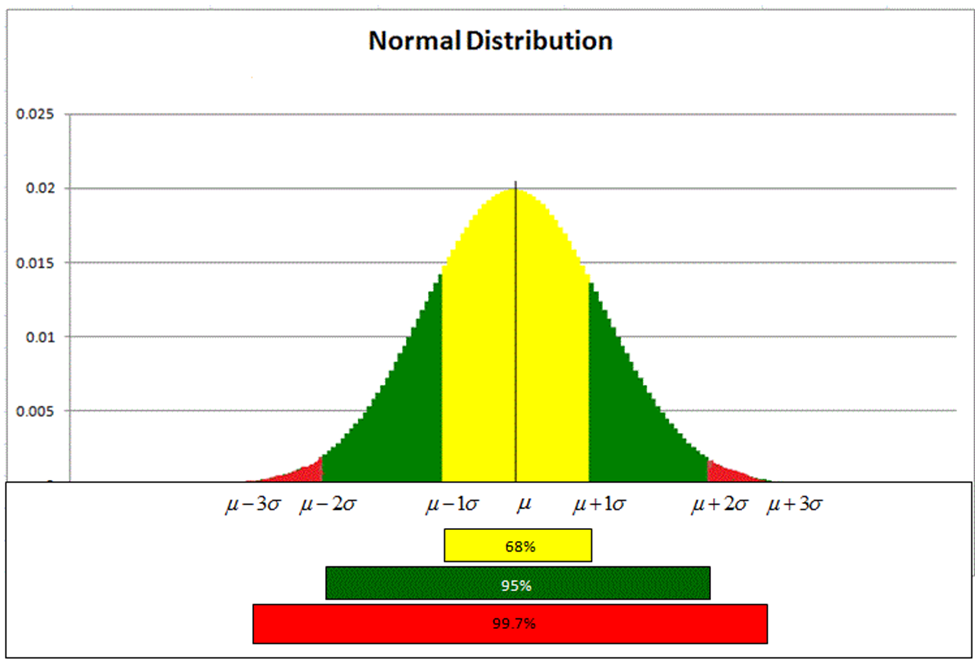
Normal Distribution Curve
Normal Distribution Curve
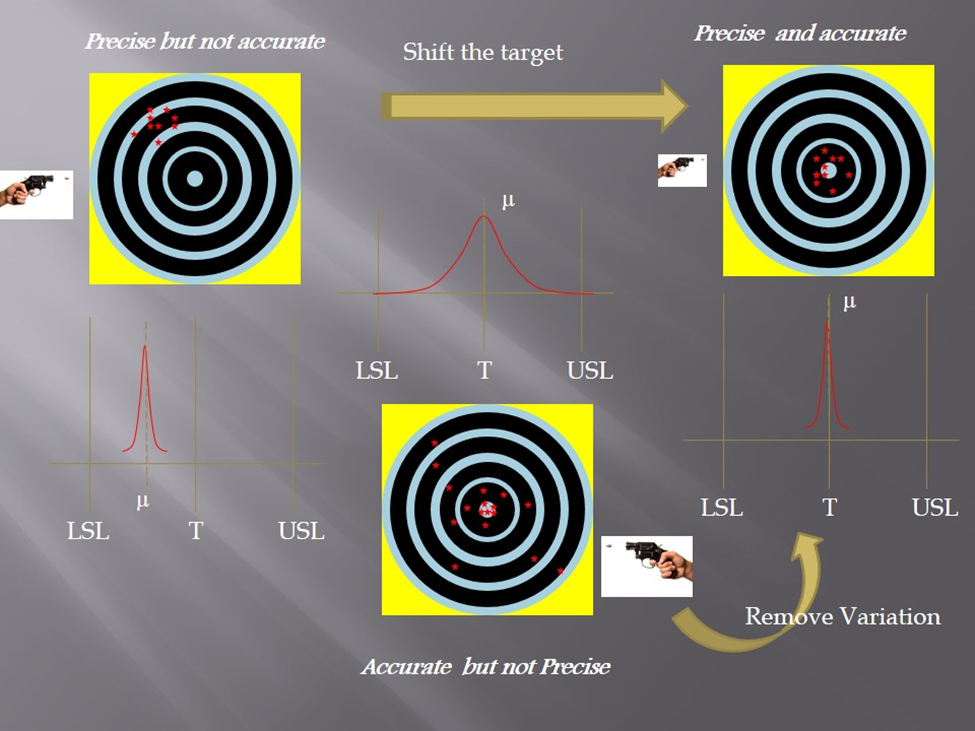
Accuracy & Precision
Accuracy & Precision
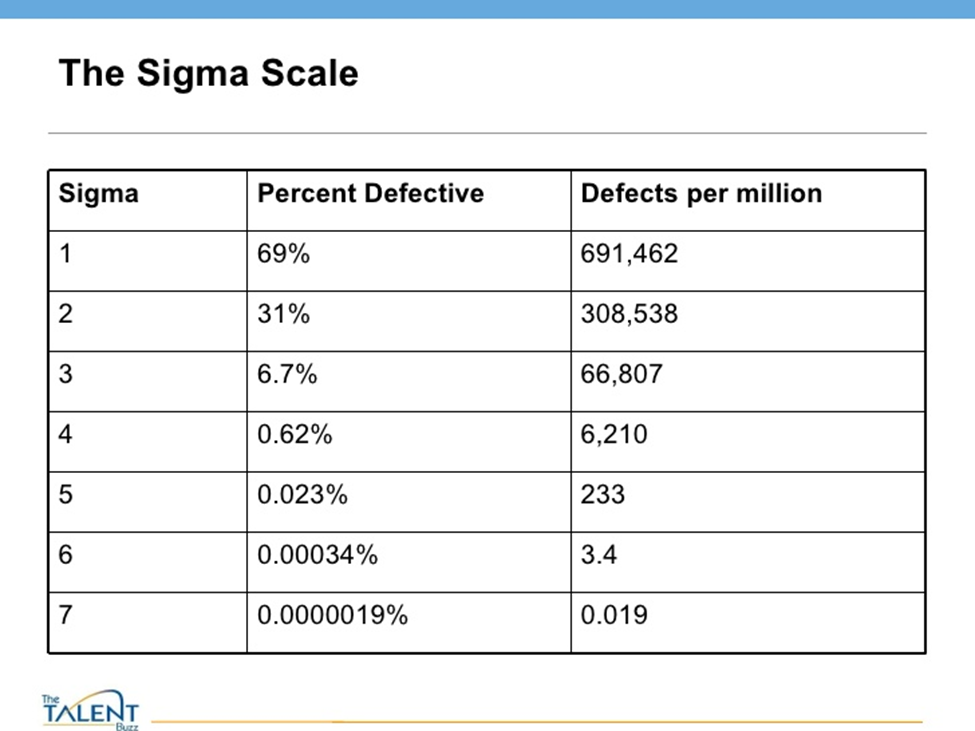
Why 3.4 DPMO ( Defect Per Million Opportunity) ?
Measured process may shift by much as 1.5 sigma, resulting in a max DPMO of 3.4
Six Sigma scale
Six Sigma scale
Harvesting the fruits of 6 s
Harvesting the fruits of 6 s

The Six Sigma DMAIC Model
Define
�Define and scope the project (including deliverables)
�Define an acceptable project schedule
�Achieve consensus on project definition
Measure
�Process definition
�Metric Definition
�Measure process baseline
�Evaluate Measurement System
Analysis
�Analyze value stream
�Analyze source of variation
�Determine process drivers
Improve
�Generate improvement ideas
�Prioritize improvement opportunities
�Define new process flow
�Define & mitigate failure modes
�Define new process factor levels
Control
�Maintain improvement
�Measure realized bottom-line impact
�Apply the knowledge elsewhere
The Six Sigma Tool Box
�SPC
�Engineering process control
�Operational procedures
�control plans
�Training
�Audit
Improve
�Brainstorming
�Affinity
�Mind mapping
�Benchmark
�FMEA
�DOE
�Six thinking hats technique
�Root cause analysis
�Process decision program chart
Analysis
�Scatter diagram
�Regression model
�Anova
�Multiple regression
�DOE
�Lean methods
�Value stream analysis
�Process cycle efficiency
�5 S
�Setup reduction
Measure
�Flowcharts
�Process Maps
�SIPOC
�Box-Whisker plots
�Cause & effect diagram
�Check sheets
�Interrelation digraph
�Pareto diagram
�Stem & leaf plot
�Gage R&R
�SPC control charts
�Histogram
�Process capability
Define
�Matrix diagrams
�Work breakdown structure
�Pareto diagram
�Process maps
�Financial analysis
�Affinity diagram
�Nominal group technique
�Prioritization matrix
�Project scheduling
�Activity network diagram
�Pert analysis
�Gannt chart
�Quality function deployment
How to apply six sigma (general concept)?